Product Description
HangZhou Yuantuo Auto Parts Manufacturing Co., Ltd was founded in 1990,which is a company specialized in production and sales of rubber parts such as center support bearing,wiper blade and torque rod bush in China.It is located in the beautiful and rich city HangZhou with a very convenient transportation near ZheJiang Kowloon Railway at the east and near National Road 106 and 308.And it covers an area of 30,000 square meters.
It continually introduces new advanced equipment and production process to enhance core competence and reduce production cost. Our products cover more than 100 models,We all along stick to the belief of quality first and customer orientation. Now our products have been exported to many countries, such as USA, Russia, Mexico, Italy, Germany, Iran, Egypt, Dubai, Malaysia, Brazil, Peru, Nigeria, Pakistan, India etc. Strict quality control and perfect after-sales service make our products widely welcomed in domestic and overseas markets.
YTK as a global manufacture specialized in auto wiper blade,our company has been ahead of the industry advanced level in rubber srtip technology after more tan 10 years of continuous development and technolgical inovation.And we are always pursing “cost-effective product ” and provide the cutstomers with safe and high quality wiper as the core idea of our company.We laid a CZPT foundation for cooperation by continuous innowation of patend products.Our products cover a compleat range of models and non-standard products could be cus-tomized.Our company always sticks to the service objective of keeping the customers satisfied .Hope that YTK could have common development and share succession to create a beautiful future together with you .
YTK Shaft Coupling Series
YOU COULD GET (Cooperation with us):
1 More than 360 types of models,expand your product catalog.
2 More better price than the trading company.
3 Support mould development help you CZPT the market opportunity.
4 Stock a lot of product mold, save the cost of developing mold for you.
5 Fast delivery!
6. Production capacity: 60,000-80,000 PCS/ month.
FAQ
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
Generally, we pack our goods in neutral boxes and brown cartons or as your demand.
If you have legally registered patent,we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
EXW, FOB, CIF, CFR
Q3. How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 10 to 30 days after receiving your advance payment.
The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q4. Do you test all your goods before delivery?
Yes, we have 100% test before delivery.
Q5. What is your sample policy?
We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the sample cost and the courier cost.
Q6. How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
1. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers’ benefit;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them, no matter where they come from.
| After-sales Service: | Best After-Sale Service |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Material: | Rubber |
| Transport Package: | as Your Demand |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What Is a Coupling?
A coupling is a device that connects two shafts together. It transmits power from one to the other and is used to join rotating equipment. It can also allow for some degree of misalignment and end movement. It is used in mechanical engineering and manufacturing. To learn more about couplings, read this article.
Mechanical connection between two objectsThe present invention relates to a method and assembly for forming a mechanical connection between two objects. The methods of this invention are suitable for connecting both solid and hollow objects. For example, the method can be used to make mechanical connections between two cylinders. This method is particularly useful for connecting two cylinders that are positioned near each other.
Absorbs vibration
A coupling insert is a part of a vehicle’s drivetrain that absorbs vibrations. These inserts are designed to prevent couplings from moving out of phase. However, the coupling inserts themselves can wear out and need to be replaced. Universal joints are an alternative if the coupling is out of phase by more than one degree. In addition, internal bearings in the coupling need to be lubricated and replaced when they begin to show signs of wear.
Another embodiment of the invention includes a flexible coupling 25 that includes rearwardly-extending lugs that extend toward the coupling member 23. These lugs interdigitate with corresponding lugs on the coupling member 23. They are spaced circumferentially. A first elastic member 28 is interposed between lugs 26 and 27, and is adapted to yield in a counterclockwise direction. As a result, it absorbs torsional vibrations.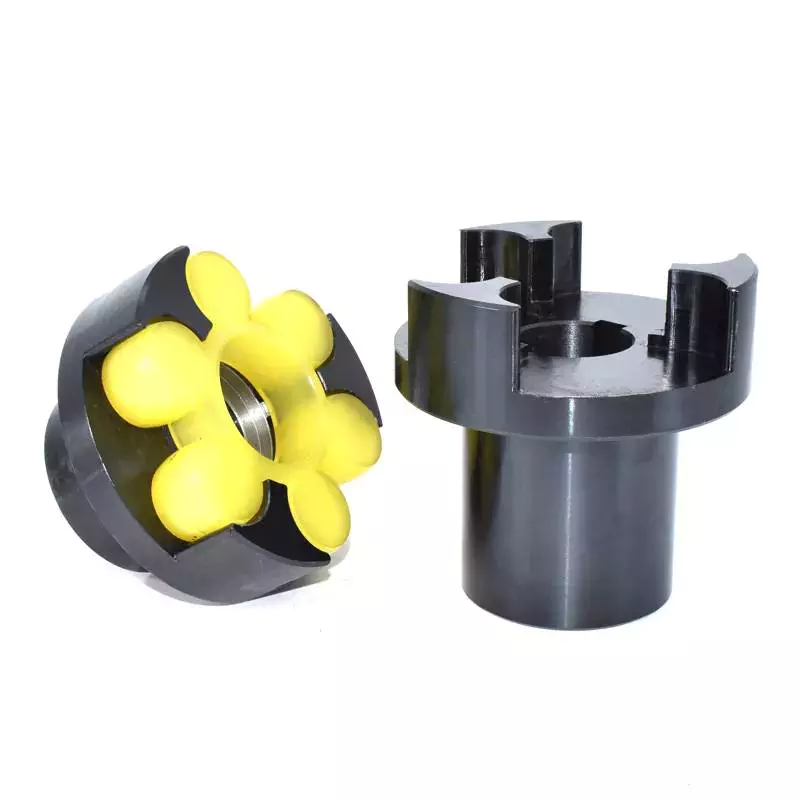
Blocks heat transfer
Thermal coupling occurs when a solid block is thermally coupled to the air or fluid passing through it. The amount of heat transferred through a solid block depends on the heat transfer coefficients of the materials. This paper presents a numerical model to understand how heat transfers through different block materials. This work also describes the thermal resistance network for a one-dimensional block.
In some cases, thermal coupling increases the heat transfer mechanism. As illustrated in FIG. 1D, a heatpipe coupler 112 couples two heatpipes 110-1 and 110-2. This configuration allows the pipes to be coupled to the heat source and to the condenser. In addition, the heat pipe couplers may have bellows at the ends to help facilitate linear motion.
Thermal coupling is achieved by ensuring that at least one block is made of a material with a lower thermal expansion coefficient than the annulus. Ideally, the block’s mean thermal expansion coefficient is at least twenty percent lower than the annulus’s mean thermal expansion coefficient. This ensures that the thermal coupling between the two parts is as efficient as possible.
Another type of thermal coupling is achieved by using flexible elements. These are often washers or springs. These components allow the blocks to maintain physical contact with the post 55, which means that the heat transfer is more efficient even at higher temperatures. The flexibility of these elements also makes it possible to choose an element that will not impede assembly.
Protects rotating equipment
A reliable, long-lasting coupling system can reduce the risk of damage to rotating equipment. Designed to protect against torque overload and wear, Voith torque-limiting couplings provide outstanding safety and reliability. As a result, they can deliver maximum performance and minimize equipment downtime. In addition to their long-term benefits, these solutions are ideal for applications where safety and reliability are of paramount importance.
A good coupling provides many advantages, including the ability to transmit power, compensate for axial movement, and absorb shock. It is essential to choose the proper coupling for your application based on the basic conditions of your rotating equipment. For example, if you have two shafts with parallel rotation axes, you should choose a parallel coupling. Otherwise, you should use an angular coupling.
Torque-limiting couplings can also provide protection for rotating equipment by disengaging at a specific torque level. This protects the drive shaft from undergoing catastrophic failure. Torque limiters are particularly helpful for high-value equipment. By preventing catastrophic failure, you can avoid expensive repairs and minimize equipment downtime.
Coupling guards are easy to install and provide effective protection for rotating equipment. These covers are made of sheet metal bent to fit over the shaft. They are durable and easy to remove when necessary. This type of guard can prevent employees from catching their hands, tools, or loose clothing on motor coupling components.

editor by CX 2023-08-02
China best Cardan Shafts for Machinery Parts with Great quality
Product Description
SWC-I Series-Light-Duty Designs Cardan shaft
Designs
Data and Size of SWC-I Series Universal Joint Couplings
1. Notations:
L=Standard length, or compressed length for designs with length compensation;
LV=Length compensation;
M=Weight;
Tn=Nominal torque(Yield torque 50% over Tn);
TF=Fatigue torque, I. E. Permissible torque as determined according to the fatigue strength
Under reversing loads;
β=Maximum deflection angle;
MI=weight per 100mm tube
2. Millimeters are used as measurement units except where noted;
3. Please consult us for customizations regarding length, length compensation and
Flange connections.
Standard Length Splined Shafts
Standard Length Splined Shafts are made from Mild Steel and are perfect for most repair jobs, custom machinery building, and many other applications. All stock splined shafts are 2-3/4 inches in length, and full splines are available in any length, with additional materials and working lengths available upon request and quotation. CZPT Manufacturing Company is proud to offer these standard length shafts.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are splined
There are 2 common disc brake mounting interfaces, splined and center lock. Disc brakes with splined interfaces are more common. They are usually easier to install. The center lock system requires a tool to remove the locking ring on the disc hub. Six-bolt rotors are easier to install and require only 6 bolts. The center lock system is commonly used with performance road bikes.
Post mount disc brakes require a post mount adapter, while flat mount disc brakes do not. Post mount adapters are more common and are used for carbon mountain bikes, while flat mount interfaces are becoming the norm on road and gravel bikes. All disc brake adapters are adjustable for rotor size, though. Road bikes usually use 160mm rotors while mountain bikes use rotors that are 180mm or 200mm.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helical splined
A helical splined disc brake mounting interface is designed with a splined connection between the hub and brake disc. This splined connection allows for a relatively large amount of radial and rotational displacement between the disc and hub. A loosely splined interface can cause a rattling noise due to the movement of the disc in relation to the hub.
The splines on the brake disc and hub are connected via an air gap. The air gap helps reduce heat conduction from the brake disc to the hub. The present invention addresses problems of noise, heat, and retraction of brake discs at the release of the brake. It also addresses issues with skewing and dragging. If you’re unsure whether this type of mounting interface is right for you, consult your mechanic.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helix-splined may be used in conjunction with other components of a wheel. They are particularly useful in disc brake mounting interfaces for hub-to-hub assemblies. The spacer elements, which are preferably located circumferentially, provide substantially the same function no matter how the brake disc rotates. Preferably, 3 spacer elements are located around the brake disc. Each of these spacer elements has equal clearance between the splines of the brake disc and the hub.
Spacer elements 6 include a helical spring portion 6.1 and extensions in tangential directions that terminate in hooks 6.4. These hooks abut against the brake disc 1 in both directions. The helical spring portion 5.1 and 6.1 have stiffness enough to absorb radial impacts. The spacer elements are arranged around the circumference of the intermeshing zone.
A helical splined disc mount includes a stabilizing element formed as a helical spring. The helical spring extends to the disc’s splines and teeth. The ends of the extension extend in opposite directions, while brackets at each end engage with the disc’s splines and teeth. This stabilizing element is positioned axially over the disc’s width.
Helical splined disc brake mounting interfaces are popular in bicycles and road bicycles. They’re a reliable, durable way to mount your brakes. Splines are widely used in aerospace, and have a higher fatigue life and reliability. The interfaces between the splined disc brake and BB spindle are made from aluminum and acetate.
As the splined hub mounts the disc in a helical fashion, the spring wire and disc 2 will be positioned in close contact. As the spring wire contacts the disc, it creates friction forces that are evenly distributed throughout the disc. This allows for a wide range of axial motion. Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helical splined have higher strength and stiffness than their counterparts.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helically splined can have a wide range of splined surfaces. The splined surfaces are the most common type of disc brake mounting interfaces. They are typically made of stainless steel or aluminum and can be used for a variety of applications. However, a splined disc mount will not support a disc with an oversized brake caliper.


China factory 3741-2203010, Uaz Propeller Shafts, Drive Shafts, Cardan Shafts wholesaler
Product Description
HangZhou Hua Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Auto Parts Co., Ltd is located in the beautiful HangZhou, China. The transportation is very covenient as it closed to CZPT international air port and ZheJiang , and HangZhou freeway in the golden area of the yangtze River Delta.
Our company is a monern enterprise that combines development disign, manufacturer, sale and service, and it’s products including to :
Russian Drive shaft, weld yoke, Flange yoke, spline yoke, slip joints, spline shafts, sleeve tube
Cardan shafts, includng to UAZ, GAZ, MAN, LADA.
PTO Shaft, pin yoke, inner yoke, outer yoke,
Off-Highway Cardan Shafts,
Universal joints, Cross, U-Joints.
MECHANICS Universal joints, CZPT style u-joints,
Tractor spare parts, MTZ spare parts.
Which are sold in more than 20 Previones, cities and automomous regiion in china and many other Country, in USA and Germany and Italy and Poland, and Russian, and North american and Africa and East-south asia and etc.
With the establishment of modern enterprise management system in the company that employs many people of different skills, our company is becoming more haman-oriented, information-based and interenationalized. The introduction of ISO9
The Benefits of Spline Couplings for Disc Brake Mounting Interfaces
Spline couplings are commonly used for securing disc brake mounting interfaces. Spline couplings are often used in high-performance vehicles, aeronautics, and many other applications. However, the mechanical benefits of splines are not immediately obvious. Listed below are the benefits of spline couplings. We’ll discuss what these advantages mean for you. Read on to discover how these couplings work.
Disc brake mounting interfaces are splined
There are 2 common disc brake mounting interfaces – splined and six-bolt. Splined rotors fit on splined hubs; six-bolt rotors will need an adapter to fit on six-bolt hubs. The six-bolt method is easier to maintain and may be preferred by many cyclists. If you’re thinking of installing a disc brake system, it is important to know how to choose the right splined and center lock interfaces.
Aerospace applications
The splines used for spline coupling in aircraft are highly complex. While some previous researches have addressed the design of splines, few publications have tackled the problem of misaligned spline coupling. Nevertheless, the accurate results we obtained were obtained using dedicated simulation tools, which are not commercially available. Nevertheless, such tools can provide a useful reference for our approach. It would be beneficial if designers could use simple tools for evaluating contact pressure peaks. Our analytical approach makes it possible to find answers to such questions.
The design of a spline coupling for aerospace applications must be accurate to minimize weight and prevent failure mechanisms. In addition to weight reduction, it is necessary to minimize fretting fatigue. The pressure distribution on the spline coupling teeth is a significant factor in determining its fretting fatigue. Therefore, we use analytical and experimental methods to examine the contact pressure distribution in the axial direction of spline couplings.
The teeth of a spline coupling can be categorized by the type of engagement they provide. This study investigates the position of resultant contact forces in the teeth of a spline coupling when applied to pitch diameter. Using FEM models, numerical results are generated for nominal and parallel offset misalignments. The axial tooth profile determines the behavior of the coupling component and its ability to resist wear. Angular misalignment is also a concern, causing misalignment.
In order to assess wear damage of a spline coupling, we must take into consideration the impact of fretting on the components. This wear is caused by relative motion between the teeth that engage them. The misalignment may be caused by vibrations, cyclical tooth deflection, or angular misalignment. The result of this analysis may help designers improve their spline coupling designs and develop improved performance.
CZPT polyimide, an abrasion-resistant polymer, is a popular choice for high-temperature spline couplings. This material reduces friction and wear, provides a low friction surface, and has a low wear rate. Furthermore, it offers up to 50 times the life of metal on metal spline connections. For these reasons, it is important to choose the right material for your spline coupling.
High-performance vehicles
A spline coupler is a device used to connect splined shafts. A typical spline coupler resembles a short pipe with splines on either end. There are 2 basic types of spline coupling: single and dual spline. One type attaches to a drive shaft, while the other attaches to the gearbox. While spline couplings are typically used in racing, they’re also used for performance problems.
The key challenge in spline couplings is to determine the optimal dimension of spline joints. This is difficult because no commercial codes allow the simulation of misaligned joints, which can destroy components. This article presents analytical approaches to estimating contact pressures in spline connections. The results are comparable with numerical approaches but require special codes to accurately model the coupling operation. This research highlights several important issues and aims to make the application of spline couplings in high-performance vehicles easier.
The stiffness of spline assemblies can be calculated using tooth-like structures. Such splines can be incorporated into the spline joint to produce global stiffness for torsional vibration analysis. Bearing reactions are calculated for a certain level of misalignment. This information can be used to design bearing dimensions and correct misalignment. There are 3 types of spline couplings.
Major diameter fit splines are made with tightly controlled outside diameters. This close fit provides concentricity transfer from the male to the female spline. The teeth of the male spline usually have chamfered tips and clearance with fillet radii. These splines are often manufactured from billet steel or aluminum. These materials are renowned for their strength and uniform grain created by the forging process. ANSI and DIN design manuals define classes of fit.
Disc brake mounting interfaces
A spline coupling for disc brake mounting interfaces is a type of hub-to-brake-disc mount. It is a highly durable coupling mechanism that reduces heat transfer from the disc to the axle hub. The mounting arrangement also isolates the axle hub from direct contact with the disc. It is also designed to minimize the amount of vehicle downtime and maintenance required to maintain proper alignment.
Disc brakes typically have substantial metal-to-metal contact with axle hub splines. The discs are held in place on the hub by intermediate inserts. This metal-to-metal contact also aids in the transfer of brake heat from the brake disc to the axle hub. Spline coupling for disc brake mounting interfaces comprises a mounting ring that is either a threaded or non-threaded spline.
During drag brake experiments, perforated friction blocks filled with various additive materials are introduced. The materials included include Cu-based powder metallurgy material, a composite material, and a Mn-Cu damping alloy. The filling material affects the braking interface’s wear behavior and friction-induced vibration characteristics. Different filling materials produce different types of wear debris and have different wear evolutions. They also differ in their surface morphology.
Disc brake couplings are usually made of 2 different types. The plain and HD versions are interchangeable. The plain version is the simplest to install, while the HD version has multiple components. The two-piece couplings are often installed at the same time, but with different mounting interfaces. You should make sure to purchase the appropriate coupling for your vehicle. These interfaces are a vital component of your vehicle and must be installed correctly for proper operation.
Disc brakes use disc-to-hub elements that help locate the forces and displace them to the rim. These elements are typically made of stainless steel, which increases the cost of manufacturing the disc brake mounting interface. Despite their benefits, however, the high braking force loads they endure are hard on the materials. Moreover, excessive heat transferred to the intermediate elements can adversely affect the fatigue life and long-term strength of the brake system.


China Hot selling Cardan Shafts (31601-2203010) near me manufacturer
Product Description
Russian drive shaft and components, UAZ, GAZ, GAZIL, ZIL, KAMAZ, MAN,
| 3303-10 | Вал карданный заднего моста на УАЗ 31512 с редукторными мостами ( для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» с 5-ст. КПП ADS-BGW) |
| 2206—–10 | Вал карданный заднего моста для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» 31512,31519 c 4-х ст. КПП |
| 3151-20 | Вал карданный заднего моста для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» 31512 с мостами “Тимкен” (для а/м с 5-ст. КПП ADS-BGW) |
| 3151-30 | Вал карданный заднего моста для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» 31519 с 5-ти ст. КПП |
| 3160—–10 | Вал карданный заднего моста для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» 3741, 2206, 3303,3909,3962 “ЕВРО” с мостами «Спайсер» |
| 3163–10 | Передача карданная 3-х опорная для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» 2360 |
| 2363–10 | Передача карданная 3-х опорная для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» 3163 ,3162 |
| 3151—–10 | Вал карданный переднего моста для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» 3741, 2206, 3303,3909,3962 “ЕВРО” с мостами «Спайсер» |
| 3303-10 | Вал карданный переднего моста для а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» 452 с 5-ти ст. КПП |
| 3151—10 | Вал карданный переднего моста для грузового ряда а/м производства ОАО «УАЗ» с инжекторным двигателем ЕВРО -4 , под гибридные мосты (на 5-и ст. КПП) |
| Крестовина карданного вала с подшипниками и стопорными кольцами | |
| опора промежуточная карданного вала | |
| 3 | |
| 3160-22 0571 1 | |
| 3 | |
| 3-10 | |
| -10 | |
| -10 | |
| 3 | |
The Different Types of Splines in a Splined Shaft
A splined shaft is a machine component with internal and external splines. The splines are formed in 4 different ways: Involute, Parallel, Serrated, and Ball. You can learn more about each type of spline in this article. When choosing a splined shaft, be sure to choose the right 1 for your application. Read on to learn about the different types of splines and how they affect the shaft’s performance.
Involute splines
Involute splines in a splined shaft are used to secure and extend mechanical assemblies. They are smooth, inwardly curving grooves that resist separation during operation. A shaft with involute splines is often longer than the shaft itself. This feature allows for more axial movement. This is beneficial for many applications, especially in a gearbox.
The involute spline is a shaped spline, similar to a parallel spline. It is angled and consists of teeth that create a spiral pattern that enables linear and rotatory motion. It is distinguished from other splines by the serrations on its flanks. It also has a flat top. It is a good option for couplers and other applications where angular movement is necessary.
Involute splines are also called involute teeth because of their shape. They are flat on the top and curved on the sides. These teeth can be either internal or external. As a result, involute splines provide greater surface contact, which helps reduce stress and fatigue. Regardless of the shape, involute splines are generally easy to machine and fit.
Involute splines are a type of splines that are used in splined shafts. These splines have different names, depending on their diameters. An example set of designations is for a 32-tooth male spline, a 2,500-tooth module, and a 30 degree pressure angle. An example of a female spline, a fillet root spline, is used to describe the diameter of the splined shaft.
The effective tooth thickness of splines is dependent on the number of keyways and the type of spline. Involute splines in splined shafts should be designed to engage 25 to 50 percent of the spline teeth during the coupling. Involute splines should be able to withstand the load without cracking.
Parallel splines
Parallel splines are formed on a splined shaft by putting 1 or more teeth into another. The male spline is positioned at the center of the female spline. The teeth of the male spline are also parallel to the shaft axis, but a common misalignment causes the splines to roll and tilt. This is common in many industrial applications, and there are a number of ways to improve the performance of splines.
Typically, parallel splines are used to reduce friction in a rotating part. The splines on a splined shaft are narrower on the end face than the interior, which makes them more prone to wear. This type of spline is used in a variety of industries, such as machinery, and it also allows for greater efficiency when transmitting torque.
Involute splines on a splined shaft are the most common. They have equally spaced teeth, and are therefore less likely to crack due to fatigue. They also tend to be easy to cut and fit. However, they are not the best type of spline. It is important to understand the difference between parallel and involute splines before deciding on which spline to use.
The difference between splined and involute splines is the size of the grooves. Involute splines are generally larger than parallel splines. These types of splines provide more torque to the gear teeth and reduce stress during operation. They are also more durable and have a longer life span. And because they are used on farm machinery, they are essential in this type of application.
Serrated splines
A Serrated Splined Shaft has several advantages. This type of shaft is highly adjustable. Its large number of teeth allows large torques, and its shorter tooth width allows for greater adjustment. These features make this type of shaft an ideal choice for applications where accuracy is critical. Listed below are some of the benefits of this type of shaft. These benefits are just a few of the advantages. Learn more about this type of shaft.
The process of hobbing is inexpensive and highly accurate. It is useful for external spline shafts, but is not suitable for internal splines. This type of process forms synchronized shapes on the shaft, reducing the manufacturing cycle and stabilizing the relative phase between spline and thread. It uses a grinding wheel to shape the shaft. CZPT Manufacturing has a large inventory of Serrated Splined Shafts.
The teeth of a Serrated Splined Shaft are designed to engage with the hub over the entire circumference of the shaft. The teeth of the shaft are spaced uniformly around the spline, creating a multiple-tooth point of contact over the entire length of the shaft. The results of these analyses are usually satisfactory. But there are some limitations. To begin with, the splines of the Serrated Splined Shaft should be chosen carefully. If the application requires large-scale analysis, it may be necessary to modify the design.
The splines of the Serrated Splined Shaft are also used for other purposes. They can be used to transmit torque to another device. They also act as an anti-rotational device and function as a linear guide. Both the design and the type of splines determine the function of the Splined Shaft. In the automobile industry, they are used in vehicles, aerospace, earth-moving machinery, and many other industries.
Ball splines
The invention relates to a ball-spinned shaft. The shaft comprises a plurality of balls that are arranged in a series and are operatively coupled to a load path section. The balls are capable of rolling endlessly along the path. This invention also relates to a ball bearing. Here, a ball bearing is 1 of the many types of gears. The following discussion describes the features of a ball bearing.
A ball-splined shaft assembly comprises a shaft with at least 1 ball-spline groove and a plurality of circumferential step grooves. The shaft is held in a first holding means that extends longitudinally and is rotatably held by a second holding means. Both the shaft and the first holding means are driven relative to 1 another by a first driving means. It is possible to manufacture a ball-splined shaft in a variety of ways.
A ball-splined shaft features a nut with recirculating balls. The ball-splined nut rides in these grooves to provide linear motion while preventing rotation. A splined shaft with a nut that has recirculating balls can also provide rotary motion. A ball splined shaft also has higher load capacities than a ball bushing. For these reasons, ball splines are an excellent choice for many applications.
In this invention, a pair of ball-spinned shafts are housed in a box under a carrier device 40. Each of the 2 shafts extends along a longitudinal line of arm 50. One end of each shaft is supported rotatably by a slide block 56. The slide block also has a support arm 58 that supports the center arm 50 in a cantilever fashion.
Sector no-go gage
A no-go gauge is a tool that checks the splined shaft for oversize. It is an effective way to determine the oversize condition of a splined shaft without removing the shaft. It measures external splines and serrations. The no-go gage is available in sizes ranging from 19mm to 130mm with a 25mm profile length.
The sector no-go gage has 2 groups of diametrally opposed teeth. The space between them is manufactured to a maximum space width and the tooth thickness must be within a predetermined tolerance. This gage would be out of tolerance if the splines were measured with a pin. The dimensions of this splined shaft can be found in the respective ANSI or DIN standards.
The go-no-go gage is useful for final inspection of thread pitch diameter. It is also useful for splined shafts and threaded nuts. The thread of a screw must match the contour of the go-no-go gage head to avoid a no-go condition. There is no substitute for a quality machine. It is an essential tool for any splined shaft and fastener manufacturer.
The NO-GO gage can detect changes in tooth thickness. It can be calibrated under ISO17025 standards and has many advantages over a non-go gage. It also gives a visual reference of the thickness of a splined shaft. When the teeth match, the shaft is considered ready for installation. It is a critical process. In some cases, it is impossible to determine the precise length of the shaft spline.
The 45-degree pressure angle is most commonly used for axles and torque-delivering members. This pressure angle is the most economical in terms of tool life, but the splines will not roll neatly like a 30 degree angle. The 45-degree spline is more likely to fall off larger than the other two. Oftentimes, it will also have a crowned look. The 37.5 degree pressure angle is a compromise between the other 2 pressure angles. It is often used when the splined shaft material is harder than usual.


China Hot selling Aluminium Stainless Steel Machinery Parts CNC Turning Drive Hollow Shafts near me shop
Product Description
At CZPT Industry, we use the latest machining technology with a wide range of capabilities to meet your demands. Our manufacturing facilities include 3-5 axis milling, lathes, grinding, etc, and state of the art metrology. With these machines, we produce complex parts in the most efficient and accurate way. Our manufacturing capabilities allow
us to develop your part from prototype to mass production for the most precise of jobs.
| Processing Method | CNC Milling, CNC Turning, Turning-Milling Machining, Micro Machining, Grinding, Boring, Tapping. |
| Material | Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, Carbon Steel, Free-cutting Steel, Brass, Copper, Aluminum, POM, PTFE. |
| Finish Treatment | Polishing, Sand Blasting, Anodizing, Zinc Plating, Nickel Plating, Blackening, QPQ, Painting, etc.. |
| Tech. Standard | ANSI, ASTM, DIN, JIS, BS, GB, ISO, etc.. |
| Application | Medical, Aerospace, Millitary, Instrument, Optics, Food Equipment, AUTO Parts, Furniture, etc.. |
Precision Machining is the most important sector in CZPT Industry, we have been a trusted manufacturing supplier in this field for over 15 years. We have built an impeccable reputation on quality, customer service and utilizing state-of-the-art equipment. Our expertise has made us the Best in Quality and Innovation.
Machining Facilities
| Equipment Description | Workpiece Dimensions | Processing Accuracy | Quantities | Brand |
| 3-axis machining center | Max. 1000 x 1200mm | +/-0.01mm | 6 | DMG |
| 4-axis machining center | Max. 1000 x 1500mm | +/-0.01mm | 4 | DMG |
| 5-axis machining center | Max. 1000 x 1500mm | +/-0.01mm | 2 | DMG |
| CNC lathe | Max. diameter 100mm | +/-0.01mm | 20 | SMTCL |
| General lathe | Max. diameter 500mm | +/-0.05mm | 2 | SMTCL |
| Turning-Milling machine | Max. diameter 100mm | +/-0.01mm | 6 | DMG |
| Longitudinal lathe | Max. diameter 30mm | +/-0.01mm | 6 | TSUGAMI |
| Automatic lathe | Max. diameter 20mm | +/-0.02mm | 30 | TY |
| CNC Swiss Lathe | Max. diameter 20mm | +/-0.01mm | 6 | TSUGAMI |
Other assist equipments include:
Milling machine, Drilling machine, Centerless Grinding machine, External Cylindrical Grinding machine, etc.
Inspection equipment:
Vernier Caliper, Micrometer, Height Gage, Hardness Tester, Two-dimensional image measuring instrument, TESA Micro-Hite 300, Mitutoyo surface Roughness Tester,
Mitutoyo CMM and Ultrasonic Cleaner.
FAQ
Q1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
Manufacturer.
Q2: How long is your delivery time?
Normally, the samples delivery is 10-15 days and the lead time for the official order is 30-45 days.
Q3: How long will it take to quote the RFQs?
Normally, it will take 2-3 days.
Q4: Do you provide samples?
Yes, the samples will be free if the cost is not too high.
Q5: Which countries are your target markets?
America, Canada, Europe, Australia and New Zealand.
Q6: Do you have experience of doing business with overseas customers?
Yes, we have over 10 years exporting experience and 95% of our products were exported to overseas market. We specialized in the high quality OEM parts, we are familiar with the standard of ANSI, DIN, ISO, BS, JIS, etc..
Q7: Do you have reference customers?
Yes, we have been appointed as the supplier of Parker(USA) since 2012. “Supply the top quality precision machined parts” is our management philosophy, ON TIME and EVERYTIME.
Stiffness and Torsional Vibration of Spline-Couplings
In this paper, we describe some basic characteristics of spline-coupling and examine its torsional vibration behavior. We also explore the effect of spline misalignment on rotor-spline coupling. These results will assist in the design of improved spline-coupling systems for various applications. The results are presented in Table 1.
Stiffness of spline-coupling
The stiffness of a spline-coupling is a function of the meshing force between the splines in a rotor-spline coupling system and the static vibration displacement. The meshing force depends on the coupling parameters such as the transmitting torque and the spline thickness. It increases nonlinearly with the spline thickness.
A simplified spline-coupling model can be used to evaluate the load distribution of splines under vibration and transient loads. The axle spline sleeve is displaced a z-direction and a resistance moment T is applied to the outer face of the sleeve. This simple model can satisfy a wide range of engineering requirements but may suffer from complex loading conditions. Its asymmetric clearance may affect its engagement behavior and stress distribution patterns.
The results of the simulations show that the maximum vibration acceleration in both Figures 10 and 22 was 3.03 g/s. This results indicate that a misalignment in the circumferential direction increases the instantaneous impact. Asymmetry in the coupling geometry is also found in the meshing. The right-side spline’s teeth mesh tightly while those on the left side are misaligned.
Considering the spline-coupling geometry, a semi-analytical model is used to compute stiffness. This model is a simplified form of a classical spline-coupling model, with submatrices defining the shape and stiffness of the joint. As the design clearance is a known value, the stiffness of a spline-coupling system can be analyzed using the same formula.
The results of the simulations also show that the spline-coupling system can be modeled using MASTA, a high-level commercial CAE tool for transmission analysis. In this case, the spline segments were modeled as a series of spline segments with variable stiffness, which was calculated based on the initial gap between spline teeth. Then, the spline segments were modelled as a series of splines of increasing stiffness, accounting for different manufacturing variations. The resulting analysis of the spline-coupling geometry is compared to those of the finite-element approach.
Despite the high stiffness of a spline-coupling system, the contact status of the contact surfaces often changes. In addition, spline coupling affects the lateral vibration and deformation of the rotor. However, stiffness nonlinearity is not well studied in splined rotors because of the lack of a fully analytical model.
Characteristics of spline-coupling
The study of spline-coupling involves a number of design factors. These include weight, materials, and performance requirements. Weight is particularly important in the aeronautics field. Weight is often an issue for design engineers because materials have varying dimensional stability, weight, and durability. Additionally, space constraints and other configuration restrictions may require the use of spline-couplings in certain applications.
The main parameters to consider for any spline-coupling design are the maximum principal stress, the maldistribution factor, and the maximum tooth-bearing stress. The magnitude of each of these parameters must be smaller than or equal to the external spline diameter, in order to provide stability. The outer diameter of the spline must be at least 4 inches larger than the inner diameter of the spline.
Once the physical design is validated, the spline coupling knowledge base is created. This model is pre-programmed and stores the design parameter signals, including performance and manufacturing constraints. It then compares the parameter values to the design rule signals, and constructs a geometric representation of the spline coupling. A visual model is created from the input signals, and can be manipulated by changing different parameters and specifications.
The stiffness of a spline joint is another important parameter for determining the spline-coupling stiffness. The stiffness distribution of the spline joint affects the rotor’s lateral vibration and deformation. A finite element method is a useful technique for obtaining lateral stiffness of spline joints. This method involves many mesh refinements and requires a high computational cost.
The diameter of the spline-coupling must be large enough to transmit the torque. A spline with a larger diameter may have greater torque-transmitting capacity because it has a smaller circumference. However, the larger diameter of a spline is thinner than the shaft, and the latter may be more suitable if the torque is spread over a greater number of teeth.
Spline-couplings are classified according to their tooth profile along the axial and radial directions. The radial and axial tooth profiles affect the component’s behavior and wear damage. Splines with a crowned tooth profile are prone to angular misalignment. Typically, these spline-couplings are oversized to ensure durability and safety.
Stiffness of spline-coupling in torsional vibration analysis
This article presents a general framework for the study of torsional vibration caused by the stiffness of spline-couplings in aero-engines. It is based on a previous study on spline-couplings. It is characterized by the following 3 factors: bending stiffness, total flexibility, and tangential stiffness. The first criterion is the equivalent diameter of external and internal splines. Both the spline-coupling stiffness and the displacement of splines are evaluated by using the derivative of the total flexibility.
The stiffness of a spline joint can vary based on the distribution of load along the spline. Variables affecting the stiffness of spline joints include the torque level, tooth indexing errors, and misalignment. To explore the effects of these variables, an analytical formula is developed. The method is applicable for various kinds of spline joints, such as splines with multiple components.
Despite the difficulty of calculating spline-coupling stiffness, it is possible to model the contact between the teeth of the shaft and the hub using an analytical approach. This approach helps in determining key magnitudes of coupling operation such as contact peak pressures, reaction moments, and angular momentum. This approach allows for accurate results for spline-couplings and is suitable for both torsional vibration and structural vibration analysis.
The stiffness of spline-coupling is commonly assumed to be rigid in dynamic models. However, various dynamic phenomena associated with spline joints must be captured in high-fidelity drivetrain models. To accomplish this, a general analytical stiffness formulation is proposed based on a semi-analytical spline load distribution model. The resulting stiffness matrix contains radial and tilting stiffness values as well as torsional stiffness. The analysis is further simplified with the blockwise inversion method.
It is essential to consider the torsional vibration of a power transmission system before selecting the coupling. An accurate analysis of torsional vibration is crucial for coupling safety. This article also discusses case studies of spline shaft wear and torsionally-induced failures. The discussion will conclude with the development of a robust and efficient method to simulate these problems in real-life scenarios.
Effect of spline misalignment on rotor-spline coupling
In this study, the effect of spline misalignment in rotor-spline coupling is investigated. The stability boundary and mechanism of rotor instability are analyzed. We find that the meshing force of a misaligned spline coupling increases nonlinearly with spline thickness. The results demonstrate that the misalignment is responsible for the instability of the rotor-spline coupling system.
An intentional spline misalignment is introduced to achieve an interference fit and zero backlash condition. This leads to uneven load distribution among the spline teeth. A further spline misalignment of 50um can result in rotor-spline coupling failure. The maximum tensile root stress shifted to the left under this condition.
Positive spline misalignment increases the gear mesh misalignment. Conversely, negative spline misalignment has no effect. The right-handed spline misalignment is opposite to the helix hand. The high contact area is moved from the center to the left side. In both cases, gear mesh is misaligned due to deflection and tilting of the gear under load.
This variation of the tooth surface is measured as the change in clearance in the transverse plain. The radial and axial clearance values are the same, while the difference between the 2 is less. In addition to the frictional force, the axial clearance of the splines is the same, which increases the gear mesh misalignment. Hence, the same procedure can be used to determine the frictional force of a rotor-spline coupling.
Gear mesh misalignment influences spline-rotor coupling performance. This misalignment changes the distribution of the gear mesh and alters contact and bending stresses. Therefore, it is essential to understand the effects of misalignment in spline couplings. Using a simplified system of helical gear pair, Hong et al. examined the load distribution along the tooth interface of the spline. This misalignment caused the flank contact pattern to change. The misaligned teeth exhibited deflection under load and developed a tilting moment on the gear.
The effect of spline misalignment in rotor-spline couplings is minimized by using a mechanism that reduces backlash. The mechanism comprises cooperably splined male and female members. One member is formed by 2 coaxially aligned splined segments with end surfaces shaped to engage in sliding relationship. The connecting device applies axial loads to these segments, causing them to rotate relative to 1 another.


China Standard CNC Machined High Quality High Precision Shafts with Good quality
Product Description
CNC Center milling Service
CNC Machining/Turning/Granding Service
Automatic Lathe Service
Our HangZhou Zhong Li Da Machinery Co.;,; Ltd are specialized in precision machining parts,; cnc machining parts,;production cnc machining,;custom cnc machining with customer drawing since 1995.;
Products detail
We have rich experience in manufacturing micro parts for a wide variety of industries.; Like Turning Part,;Shaft,;Machining Part,; CNC Machining Part,; Milling Part,; Hardware Accessories,; Arrow Metal Part,; Special fasteners,; Industrial Control Switch Metal Part for medical,; electronic,; fiberoptic,; microwave area,; etc.;
| Quality Assurance | ISO9001:;2008 Certified etc | ||||||||
| Materials | Aluminum Alloy:;5052 /6061/ 6063 / 2017 / 7075 / ADC12/518 etc.; | ||||||||
| Brass Alloy:;3600 /3602 / 2604 / H59 / H62 / etc.;etc.; | |||||||||
| Stainless Steel Alloy:;303 / 304 / 316 / 412 / etc.; | |||||||||
| Steel Alloy:; C45 | |||||||||
| Carbon Steel 12L14 12L15/ Die Steel / Spring Steel etc.; | |||||||||
| Special material:;Lucite / Nylon / Bakelite / POM / ABS / PP / PC / PE / PEEK / Titanium etc.; |
|||||||||
| We handle many other type of materials.; Please contact us if your required material is not listed above.; |
|||||||||
| Surface Treatment | Blacking,;polishing,;sandblasting,;anodize,;chrome plating,;zinc plating,; pickling&passivation,; vibration,;nickel plating,;tinting |
||||||||
| Inspection | Mitutotyo three-coordinate measuring machine / Mitutoyo Tool Microscope can measure up to 300mmX x 175mmY x 220mmZ |
||||||||
| File Formats | Solid Works,;Pro/Engineer,; AutoCAD(DXF,;DWG);,; PDF,;TIF ,; IGS ,; STP etc.; | ||||||||
Production Flow Chart
Factory Show
Shipping&Payment
FAQ
Q:; How soon can I get reply after send inquiry?
A:; 1.;all inquiries will be replied within 2 hours except sleeping time in China.;
2.;Our call phones standing by any calls at any time
Q:; How soon can I get samples ?
A:; Generally samples can be sent out within 7 working days after product drawing confirmed by both side.;
Q:; What file format can you accept for my products?
A:; 1.;We can accept varies format,; igs,; step,; stp,; jpg,;pdf,; dwg,; dxf and so on.;
2.;If you do not have a prepared CAD file,; we can accept a scan of a hand drawn design.;
Q:; If I don’t have drawing,; how can I get sample ?
A:; If you don’t have any drawing,;you can send us your sample,; we will scan it and make 2D and 3D drawing first,; then make sample for you.;
Q:; What are many common materials that you use in projects?
A:; Aluminum,;Stainless Steel,; Carbon Steel,; Copper,; Plastics,; Titanium and PEEK
Q:; What’s your MOQ(minimum order quantity);
A:; We don’t have MOQ,; you are welcome to send us trial order to test our quality and service.;
Q:; What’s the payment term do you accept?
A:; EXW/FOB HangZhou,; paid by T/T,; Paypal,; Western Union.;
Q:; What kind of machining we excel in?
A:; Included all kind of machining parts.;
Standard Length Splined Shafts
Standard Length Splined Shafts are made from Mild Steel and are perfect for most repair jobs, custom machinery building, and many other applications. All stock splined shafts are 2-3/4 inches in length, and full splines are available in any length, with additional materials and working lengths available upon request and quotation. CZPT Manufacturing Company is proud to offer these standard length shafts.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are splined
There are 2 common disc brake mounting interfaces, splined and center lock. Disc brakes with splined interfaces are more common. They are usually easier to install. The center lock system requires a tool to remove the locking ring on the disc hub. Six-bolt rotors are easier to install and require only 6 bolts. The center lock system is commonly used with performance road bikes.
Post mount disc brakes require a post mount adapter, while flat mount disc brakes do not. Post mount adapters are more common and are used for carbon mountain bikes, while flat mount interfaces are becoming the norm on road and gravel bikes. All disc brake adapters are adjustable for rotor size, though. Road bikes usually use 160mm rotors while mountain bikes use rotors that are 180mm or 200mm.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helical splined
A helical splined disc brake mounting interface is designed with a splined connection between the hub and brake disc. This splined connection allows for a relatively large amount of radial and rotational displacement between the disc and hub. A loosely splined interface can cause a rattling noise due to the movement of the disc in relation to the hub.
The splines on the brake disc and hub are connected via an air gap. The air gap helps reduce heat conduction from the brake disc to the hub. The present invention addresses problems of noise, heat, and retraction of brake discs at the release of the brake. It also addresses issues with skewing and dragging. If you’re unsure whether this type of mounting interface is right for you, consult your mechanic.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helix-splined may be used in conjunction with other components of a wheel. They are particularly useful in disc brake mounting interfaces for hub-to-hub assemblies. The spacer elements, which are preferably located circumferentially, provide substantially the same function no matter how the brake disc rotates. Preferably, 3 spacer elements are located around the brake disc. Each of these spacer elements has equal clearance between the splines of the brake disc and the hub.
Spacer elements 6 include a helical spring portion 6.1 and extensions in tangential directions that terminate in hooks 6.4. These hooks abut against the brake disc 1 in both directions. The helical spring portion 5.1 and 6.1 have stiffness enough to absorb radial impacts. The spacer elements are arranged around the circumference of the intermeshing zone.
A helical splined disc mount includes a stabilizing element formed as a helical spring. The helical spring extends to the disc’s splines and teeth. The ends of the extension extend in opposite directions, while brackets at each end engage with the disc’s splines and teeth. This stabilizing element is positioned axially over the disc’s width.
Helical splined disc brake mounting interfaces are popular in bicycles and road bicycles. They’re a reliable, durable way to mount your brakes. Splines are widely used in aerospace, and have a higher fatigue life and reliability. The interfaces between the splined disc brake and BB spindle are made from aluminum and acetate.
As the splined hub mounts the disc in a helical fashion, the spring wire and disc 2 will be positioned in close contact. As the spring wire contacts the disc, it creates friction forces that are evenly distributed throughout the disc. This allows for a wide range of axial motion. Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helical splined have higher strength and stiffness than their counterparts.
Disc brake mounting interfaces that are helically splined can have a wide range of splined surfaces. The splined surfaces are the most common type of disc brake mounting interfaces. They are typically made of stainless steel or aluminum and can be used for a variety of applications. However, a splined disc mount will not support a disc with an oversized brake caliper.


China Best Sales 41204-E0210, S3731-51680 Hino Drive Shafts near me manufacturer
Product Description
Procue the drive shafts, cardan shafts, and components
| STAHL | Other number |
| HFL623 | 01-379C |
| HFL622 | 01-336 |
| HLV629 | 3104Z |
| HTM621 | 04-915-1 |
| HTM622 | 04-895-1 |
| HGF631 | GR1338 |
| HTM609 | 04-898-1 |
| HTM624 | 90-4-11-1 |
| HTM628 | 90-4-311-1 |
| HTM635 | FL1096 |
| HTM630 | FL1098 |
| HTM631 | FL1097 |
| HTM627 | 04-360C |
| HPL140 | |
| HPL250 | |
| HPL400 | |
| HPL500 | |
| HPL600 | |
| HFL624 | AT1353 |
| HFL628 | AT1349 |
| HFL629 | GR1434 |
| HLV630 | LV1253 |
| HLV631 | LV1251 |
| HPT625 | PT1432 |
| HPT639 | PT1433 |
| HTM629 | FL1381 |
| HTM620 | FL1082 |
| HTM623 | S-323 |
| THM625 | FL1379 |
| HTM626 | FL1473 |
| HTM632 | FL1371 |
| HGF602 | 2-2-1697 |
| HGF603 | 3-28-537 |
| HGF613 | 2-28-357 |
| HGF614 | 90-26-27 |
| HLV609 | 2-3-14501KX |
| HPT619 | 3-53-1371 |
| HPT620 | 3-53-1361 |
How to Calculate Stiffness, Centering Force, Wear and Fatigue Failure of Spline Couplings
There are various types of spline couplings. These couplings have several important properties. These properties are: Stiffness, Involute splines, Misalignment, Wear and fatigue failure. To understand how these characteristics relate to spline couplings, read this article. It will give you the necessary knowledge to determine which type of coupling best suits your needs. Keeping in mind that spline couplings are usually spherical in shape, they are made of steel.
Involute splines
An effective side interference condition minimizes gear misalignment. When 2 splines are coupled with no spline misalignment, the maximum tensile root stress shifts to the left by 5 mm. A linear lead variation, which results from multiple connections along the length of the spline contact, increases the effective clearance or interference by a given percentage. This type of misalignment is undesirable for coupling high-speed equipment.
Involute splines are often used in gearboxes. These splines transmit high torque, and are better able to distribute load among multiple teeth throughout the coupling circumference. The involute profile and lead errors are related to the spacing between spline teeth and keyways. For coupling applications, industry practices use splines with 25 to 50-percent of spline teeth engaged. This load distribution is more uniform than that of conventional single-key couplings.
To determine the optimal tooth engagement for an involved spline coupling, Xiangzhen Xue and colleagues used a computer model to simulate the stress applied to the splines. The results from this study showed that a “permissible” Ruiz parameter should be used in coupling. By predicting the amount of wear and tear on a crowned spline, the researchers could accurately predict how much damage the components will sustain during the coupling process.
There are several ways to determine the optimal pressure angle for an involute spline. Involute splines are commonly measured using a pressure angle of 30 degrees. Similar to gears, involute splines are typically tested through a measurement over pins. This involves inserting specific-sized wires between gear teeth and measuring the distance between them. This method can tell whether the gear has a proper tooth profile.
The spline system shown in Figure 1 illustrates a vibration model. This simulation allows the user to understand how involute splines are used in coupling. The vibration model shows 4 concentrated mass blocks that represent the prime mover, the internal spline, and the load. It is important to note that the meshing deformation function represents the forces acting on these 3 components.
Stiffness of coupling
The calculation of stiffness of a spline coupling involves the measurement of its tooth engagement. In the following, we analyze the stiffness of a spline coupling with various types of teeth using 2 different methods. Direct inversion and blockwise inversion both reduce CPU time for stiffness calculation. However, they require evaluation submatrices. Here, we discuss the differences between these 2 methods.
The analytical model for spline couplings is derived in the second section. In the third section, the calculation process is explained in detail. We then validate this model against the FE method. Finally, we discuss the influence of stiffness nonlinearity on the rotor dynamics. Finally, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method. We present a simple yet effective method for estimating the lateral stiffness of spline couplings.
The numerical calculation of the spline coupling is based on the semi-analytical spline load distribution model. This method involves refined contact grids and updating the compliance matrix at each iteration. Hence, it consumes significant computational time. Further, it is difficult to apply this method to the dynamic analysis of a rotor. This method has its own limitations and should be used only when the spline coupling is fully investigated.
The meshing force is the force generated by a misaligned spline coupling. It is related to the spline thickness and the transmitting torque of the rotor. The meshing force is also related to the dynamic vibration displacement. The result obtained from the meshing force analysis is given in Figures 7, 8, and 9.
The analysis presented in this paper aims to investigate the stiffness of spline couplings with a misaligned spline. Although the results of previous studies were accurate, some issues remained. For example, the misalignment of the spline may cause contact damages. The aim of this article is to investigate the problems associated with misaligned spline couplings and propose an analytical approach for estimating the contact pressure in a spline connection. We also compare our results to those obtained by pure numerical approaches.
Misalignment
To determine the centering force, the effective pressure angle must be known. Using the effective pressure angle, the centering force is calculated based on the maximum axial and radial loads and updated Dudley misalignment factors. The centering force is the maximum axial force that can be transmitted by friction. Several published misalignment factors are also included in the calculation. A new method is presented in this paper that considers the cam effect in the normal force.
In this new method, the stiffness along the spline joint can be integrated to obtain a global stiffness that is applicable to torsional vibration analysis. The stiffness of bearings can also be calculated at given levels of misalignment, allowing for accurate estimation of bearing dimensions. It is advisable to check the stiffness of bearings at all times to ensure that they are properly sized and aligned.
A misalignment in a spline coupling can result in wear or even failure. This is caused by an incorrectly aligned pitch profile. This problem is often overlooked, as the teeth are in contact throughout the involute profile. This causes the load to not be evenly distributed along the contact line. Consequently, it is important to consider the effect of misalignment on the contact force on the teeth of the spline coupling.
The centre of the male spline in Figure 2 is superposed on the female spline. The alignment meshing distances are also identical. Hence, the meshing force curves will change according to the dynamic vibration displacement. It is necessary to know the parameters of a spline coupling before implementing it. In this paper, the model for misalignment is presented for spline couplings and the related parameters.
Using a self-made spline coupling test rig, the effects of misalignment on a spline coupling are studied. In contrast to the typical spline coupling, misalignment in a spline coupling causes fretting wear at a specific position on the tooth surface. This is a leading cause of failure in these types of couplings.
Wear and fatigue failure
The failure of a spline coupling due to wear and fatigue is determined by the first occurrence of tooth wear and shaft misalignment. Standard design methods do not account for wear damage and assess the fatigue life with big approximations. Experimental investigations have been conducted to assess wear and fatigue damage in spline couplings. The tests were conducted on a dedicated test rig and special device connected to a standard fatigue machine. The working parameters such as torque, misalignment angle, and axial distance have been varied in order to measure fatigue damage. Over dimensioning has also been assessed.
During fatigue and wear, mechanical sliding takes place between the external and internal splines and results in catastrophic failure. The lack of literature on the wear and fatigue of spline couplings in aero-engines may be due to the lack of data on the coupling’s application. Wear and fatigue failure in splines depends on a number of factors, including the material pair, geometry, and lubrication conditions.
The analysis of spline couplings shows that over-dimensioning is common and leads to different damages in the system. Some of the major damages are wear, fretting, corrosion, and teeth fatigue. Noise problems have also been observed in industrial settings. However, it is difficult to evaluate the contact behavior of spline couplings, and numerical simulations are often hampered by the use of specific codes and the boundary element method.
The failure of a spline gear coupling was caused by fatigue, and the fracture initiated at the bottom corner radius of the keyway. The keyway and splines had been overloaded beyond their yield strength, and significant yielding was observed in the spline gear teeth. A fracture ring of non-standard alloy steel exhibited a sharp corner radius, which was a significant stress raiser.
Several components were studied to determine their life span. These components include the spline shaft, the sealing bolt, and the graphite ring. Each of these components has its own set of design parameters. However, there are similarities in the distributions of these components. Wear and fatigue failure of spline couplings can be attributed to a combination of the 3 factors. A failure mode is often defined as a non-linear distribution of stresses and strains.


China Hot selling Hot Sale High Quality Metal Pin Shafts near me manufacturer
Product Description
CNC Center milling Service
CNC Machining/Turning/Granding Service
Automatic Lathe Service
Our HangZhou Zhong Li Da Machinery Co.;,; Ltd are specialized in precision machining parts,; cnc machining parts,;production cnc machining,;custom cnc machining with customer drawing since 1995.;
Products detail
We have rich experience in manufacturing micro parts for a wide variety of industries.; Like Turning Part,;Shaft,;Machining Part,; CNC Machining Part,; Milling Part,; Hardware Accessories,; Arrow Metal Part,; Special fasteners,; Industrial Control Switch Metal Part for medical,; electronic,; fiberoptic,; microwave area,; etc.;
| Quality Assurance | ISO9001:;2008 Certified etc | ||||||||
| Materials | Aluminum Alloy:;5052 /6061/ 6063 / 2017 / 7075 / ADC12/518 etc.; | ||||||||
| Brass Alloy:;3600 /3602 / 2604 / H59 / H62 / etc.;etc.; | |||||||||
| Stainless Steel Alloy:;303 / 304 / 316 / 412 / etc.; | |||||||||
| Steel Alloy:; C45 | |||||||||
| Carbon Steel 12L14 12L15/ Die Steel / Spring Steel etc.; | |||||||||
| Special material:;Lucite / Nylon / Bakelite / POM / ABS / PP / PC / PE / PEEK / Titanium etc.; |
|||||||||
| We handle many other type of materials.; Please contact us if your required material is not listed above.; |
|||||||||
| Surface Treatment | Blacking,;polishing,;sandblasting,;anodize,;chrome plating,;zinc plating,; pickling&passivation,; vibration,;nickel plating,;tinting |
||||||||
| Inspection | Mitutotyo three-coordinate measuring machine / Mitutoyo Tool Microscope can measure up to 300mmX x 175mmY x 220mmZ |
||||||||
| File Formats | Solid Works,;Pro/Engineer,; AutoCAD(DXF,;DWG);,; PDF,;TIF ,; IGS ,; STP etc.; | ||||||||
Production Flow Chart
Factory Show
Shipping&Payment
FAQ
Q:; How soon can I get reply after send inquiry?
A:; 1.;all inquiries will be replied within 2 hours except sleeping time in China.;
2.;Our call phones standing by any calls at any time
Q:; How soon can I get samples ?
A:; Generally samples can be sent out within 7 working days after product drawing confirmed by both side.;
Q:; What file format can you accept for my products?
A:; 1.;We can accept varies format,; igs,; step,; stp,; jpg,;pdf,; dwg,; dxf and so on.;
2.;If you do not have a prepared CAD file,; we can accept a scan of a hand drawn design.;
Q:; If I don’t have drawing,; how can I get sample ?
A:; If you don’t have any drawing,;you can send us your sample,; we will scan it and make 2D and 3D drawing first,; then make sample for you.;
Q:; What are many common materials that you use in projects?
A:; Aluminum,;Stainless Steel,; Carbon Steel,; Copper,; Plastics,; Titanium and PEEK
Q:; What’s your MOQ(minimum order quantity);
A:; We don’t have MOQ,; you are welcome to send us trial order to test our quality and service.;
Q:; What’s the payment term do you accept?
A:; EXW/FOB HangZhou,; paid by T/T,; Paypal,; Western Union.;
Q:; What kind of machining we excel in?
A:; Included all kind of machining parts.;
Applications of Spline Couplings
A spline coupling is a highly effective means of connecting 2 or more components. These types of couplings are very efficient, as they combine linear motion with rotation, and their efficiency makes them a desirable choice in numerous applications. Read on to learn more about the main characteristics and applications of spline couplings. You will also be able to determine the predicted operation and wear. You can easily design your own couplings by following the steps outlined below.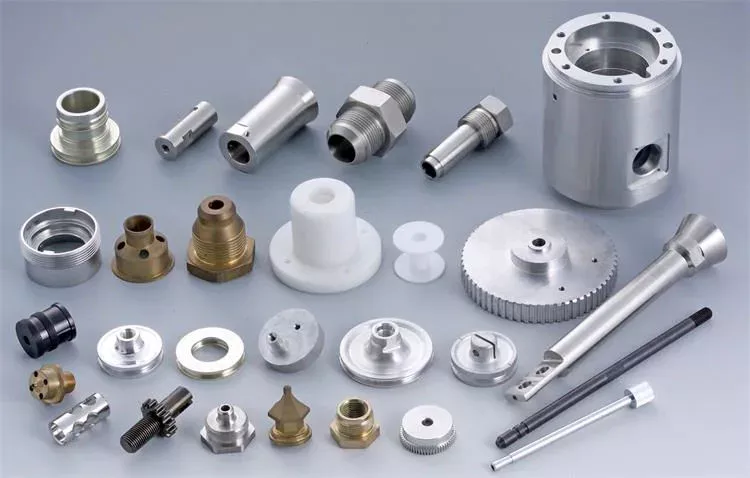
Optimal design
The spline coupling plays an important role in transmitting torque. It consists of a hub and a shaft with splines that are in surface contact without relative motion. Because they are connected, their angular velocity is the same. The splines can be designed with any profile that minimizes friction. Because they are in contact with each other, the load is not evenly distributed, concentrating on a small area, which can deform the hub surface.
Optimal spline coupling design takes into account several factors, including weight, material characteristics, and performance requirements. In the aeronautics industry, weight is an important design factor. S.A.E. and ANSI tables do not account for weight when calculating the performance requirements of spline couplings. Another critical factor is space. Spline couplings may need to fit in tight spaces, or they may be subject to other configuration constraints.
Optimal design of spline couplers may be characterized by an odd number of teeth. However, this is not always the case. If the external spline’s outer diameter exceeds a certain threshold, the optimal spline coupling model may not be an optimal choice for this application. To optimize a spline coupling for a specific application, the user may need to consider the sizing method that is most appropriate for their application.
Once a design is generated, the next step is to test the resulting spline coupling. The system must check for any design constraints and validate that it can be produced using modern manufacturing techniques. The resulting spline coupling model is then exported to an optimisation tool for further analysis. The method enables a designer to easily manipulate the design of a spline coupling and reduce its weight.
The spline coupling model 20 includes the major structural features of a spline coupling. A product model software program 10 stores default values for each of the spline coupling’s specifications. The resulting spline model is then calculated in accordance with the algorithm used in the present invention. The software allows the designer to enter the spline coupling’s radii, thickness, and orientation.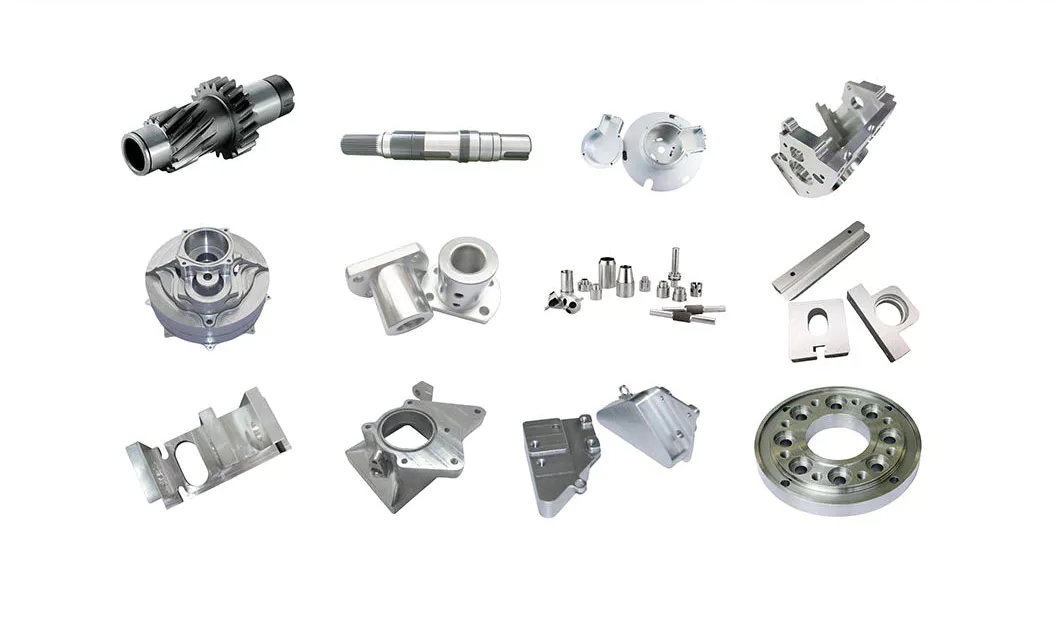
Characteristics
An important aspect of aero-engine splines is the load distribution among the teeth. The researchers have performed experimental tests and have analyzed the effect of lubrication conditions on the coupling behavior. Then, they devised a theoretical model using a Ruiz parameter to simulate the actual working conditions of spline couplings. This model explains the wear damage caused by the spline couplings by considering the influence of friction, misalignment, and other conditions that are relevant to the splines’ performance.
In order to design a spline coupling, the user first inputs the design criteria for sizing load carrying sections, including the external spline 40 of the spline coupling model 30. Then, the user specifies torque margin performance requirement specifications, such as the yield limit, plastic buckling, and creep buckling. The software program then automatically calculates the size and configuration of the load carrying sections and the shaft. These specifications are then entered into the model software program 10 as specification values.
Various spline coupling configuration specifications are input on the GUI screen 80. The software program 10 then generates a spline coupling model by storing default values for the various specifications. The user then can manipulate the spline coupling model by modifying its various specifications. The final result will be a computer-aided design that enables designers to optimize spline couplings based on their performance and design specifications.
The spline coupling model software program continually evaluates the validity of spline coupling models for a particular application. For example, if a user enters a data value signal corresponding to a parameter signal, the software compares the value of the signal entered to the corresponding value in the knowledge base. If the values are outside the specifications, a warning message is displayed. Once this comparison is completed, the spline coupling model software program outputs a report with the results.
Various spline coupling design factors include weight, material properties, and performance requirements. Weight is 1 of the most important design factors, particularly in the aeronautics field. ANSI and S.A.E. tables do not consider these factors when calculating the load characteristics of spline couplings. Other design requirements may also restrict the configuration of a spline coupling.
Applications
Spline couplings are a type of mechanical joint that connects 2 rotating shafts. Its 2 parts engage teeth that transfer load. Although splines are commonly over-dimensioned, they are still prone to fatigue and static behavior. These properties also make them prone to wear and tear. Therefore, proper design and selection are vital to minimize wear and tear on splines. There are many applications of spline couplings.
A key design is based on the size of the shaft being joined. This allows for the proper spacing of the keys. A novel method of hobbing allows for the formation of tapered bases without interference, and the root of the keys is concentric with the axis. These features enable for high production rates. Various applications of spline couplings can be found in various industries. To learn more, read on.
FE based methodology can predict the wear rate of spline couplings by including the evolution of the coefficient of friction. This method can predict fretting wear from simple round-on-flat geometry, and has been calibrated with experimental data. The predicted wear rate is reasonable compared to the experimental data. Friction evolution in spline couplings depends on the spline geometry. It is also crucial to consider the lubrication condition of the splines.
Using a spline coupling reduces backlash and ensures proper alignment of mated components. The shaft’s splined tooth form transfers rotation from the splined shaft to the internal splined member, which may be a gear or other rotary device. A spline coupling’s root strength and torque requirements determine the type of spline coupling that should be used.
The spline root is usually flat and has a crown on 1 side. The crowned spline has a symmetrical crown at the centerline of the face-width of the spline. As the spline length decreases toward the ends, the teeth are becoming thinner. The tooth diameter is measured in pitch. This means that the male spline has a flat root and a crowned spline.
Predictability
Spindle couplings are used in rotating machinery to connect 2 shafts. They are composed of 2 parts with teeth that engage each other and transfer load. Spline couplings are commonly over-dimensioned and are prone to static and fatigue behavior. Wear phenomena are also a common problem with splines. To address these issues, it is essential to understand the behavior and predictability of these couplings.
Dynamic behavior of spline-rotor couplings is often unclear, particularly if the system is not integrated with the rotor. For example, when a misalignment is not present, the main response frequency is 1 X-rotating speed. As the misalignment increases, the system starts to vibrate in complex ways. Furthermore, as the shaft orbits depart from the origin, the magnitudes of all the frequencies increase. Thus, research results are useful in determining proper design and troubleshooting of rotor systems.
The model of misaligned spline couplings can be obtained by analyzing the stress-compression relationships between 2 spline pairs. The meshing force model of splines is a function of the system mass, transmitting torque, and dynamic vibration displacement. This model holds when the dynamic vibration displacement is small. Besides, the CZPT stepping integration method is stable and has high efficiency.
The slip distributions are a function of the state of lubrication, coefficient of friction, and loading cycles. The predicted wear depths are well within the range of measured values. These predictions are based on the slip distributions. The methodology predicts increased wear under lightly lubricated conditions, but not under added lubrication. The lubrication condition and coefficient of friction are the key factors determining the wear behavior of splines.


China Professional Agricultural Tractor Flexible Pto Spine Shafts with Overrun Friction Clutch China Brand Industrial Machinery Torque Limiter Rotavator Cultivator Cardan with Great quality
Product Description
Agricultural Tractor flexible Pto spine Shafts with Overrun Friction Clutch China Brand Industrial Machinery Torque Limiter Rotavator Cultivator Cardan
The Functions of Splined Shaft Bearings
Splined shafts are the most common types of bearings for machine tools. They are made of a wide variety of materials, including metals and non-metals such as Delrin and nylon. They are often fabricated to reduce deflection. The tooth profile will become deformed with time, as the shaft is used over a long period of time. Splined shafts are available in a huge range of materials and lengths.
Functions
Splined shafts are used in a variety of applications and industries. They are an effective anti-rotational device, as well as a reliable means of transmitting torque. Other types of shafts are available, including key shafts, but splines are the most convenient for transmitting torque. The following article discusses the functions of splines and why they are a superior choice. Listed below are a few examples of applications and industries in which splines are used.
Splined shafts can be of several styles, depending on the application and mechanical system in question. The differences between splined shaft styles include the design of teeth, overall strength, transfer of rotational concentricity, sliding ability, and misalignment tolerance. Listed below are a few examples of splines, as well as some of their benefits. The difference between these styles is not mutually exclusive; instead, each style has a distinct set of pros and cons.
A splined shaft is a cylindrical shaft with teeth or ridges that correspond to a specific angular position. This allows a shaft to transfer torque while maintaining angular correspondence between tracks. A splined shaft is defined as a cylindrical member with several grooves cut into its circumference. These grooves are equally spaced around the shaft and form a series of projecting keys. These features give the shaft a rounded appearance and allow it to fit perfectly into a grooved cylindrical member.
While the most common applications of splines are for shortening or extending shafts, they can also be used to secure mechanical assemblies. An “involute spline” spline has a groove that is wider than its counterparts. The result is that a splined shaft will resist separation during operation. They are an ideal choice for applications where deflection is an issue.
A spline shaft’s radial torsion load distribution is equally distributed, unless a bevel gear is used. The radial torsion load is evenly distributed and will not exert significant load concentration. If the spline couplings are not aligned correctly, the spline connection can fail quickly, causing significant fretting fatigue and wear. A couple of papers discuss this issue in more detail.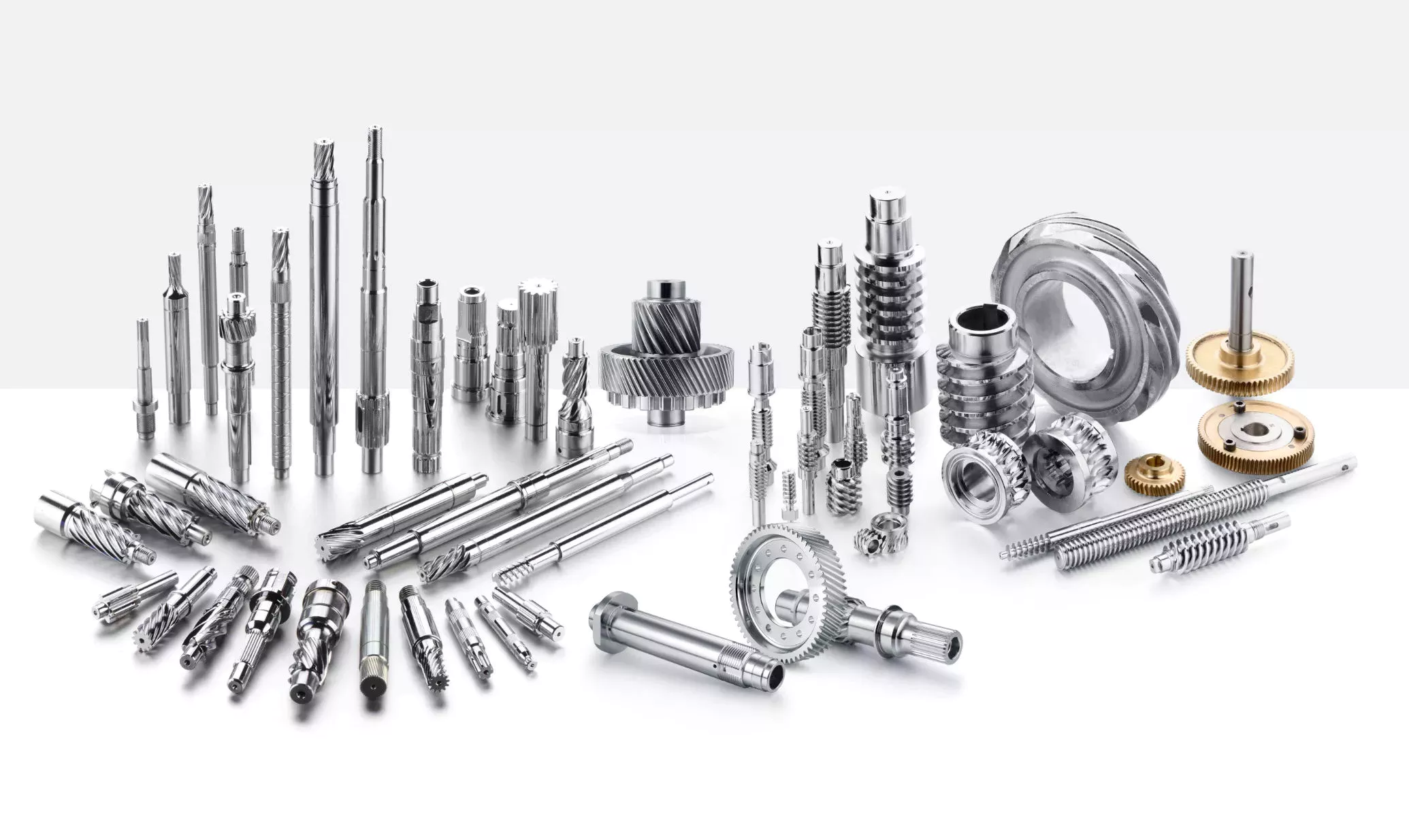
Types
There are many different types of splined shafts. Each type features an evenly spaced helix of grooves on its outer surface. These grooves are either parallel or involute. Their shape allows them to be paired with gears and interchange rotary and linear motion. Splines are often cold-rolled or cut. The latter has increased strength compared to cut spines. These types of shafts are commonly used in applications requiring high strength, accuracy, and smoothness.
Another difference between internal and external splined shafts lies in the manufacturing process. The former is made of wood, while the latter is made of steel or a metal alloy. The process of manufacturing splined shafts involves cutting furrows into the surface of the material. Both processes are expensive and require expert skill. The main advantage of splined shafts is their adaptability to a wide range of applications.
In general, splined shafts are used in machinery where the rotation is transferred to an internal splined member. This member can be a gear or some other rotary device. These types of shafts are often packaged together as a hub assembly. Cleaning and lubricating are essential to the life of these components. If you’re using them on a daily basis, you’ll want to make sure to regularly inspect them.
Crowned splines are usually involute. The teeth of these splines form a spiral pattern. They are used for smaller diameter shafts because they add strength. Involute splines are also used on instrument drives and valve shafts. Serration standards are found in the SAE. Both kinds of splines can also contain a ball bearing for high torque. The difference between the 2 types of splines is the number of teeth on the shaft.
Internal splines have many advantages over external ones. For example, an internal spline shaft can be made using a grinding wheel instead of a CNC machine. It also uses a more accurate and economical process. Furthermore, it allows for a shorter manufacturing cycle, which is essential when splining high-speed machines. In addition, it stabilizes the relative phase between the spline and thread.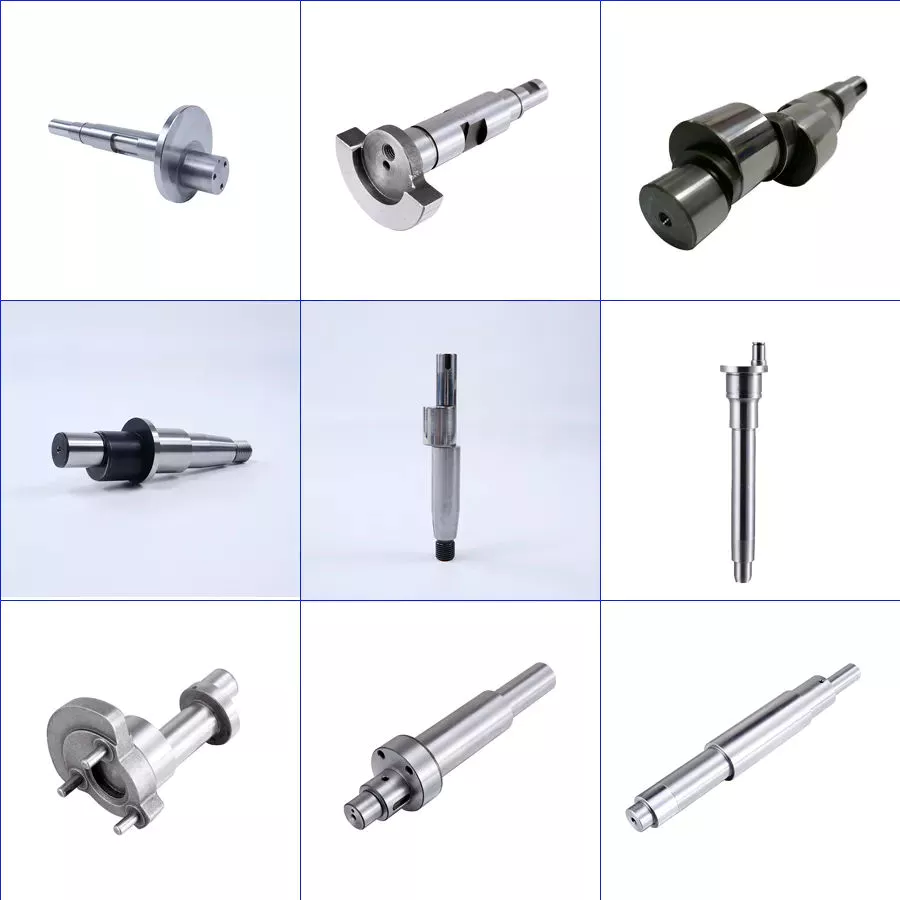
Manufacturing methods
There are several methods used to fabricate a splined shaft. Key and splined shafts are constructed from 2 separate parts that are shaped in a synchronized manner to transfer torque uniformly. Hot rolling is 1 method, while cold rolling utilizes low temperatures to form metal. Both methods enhance mechanical properties, surface finishes, and precision. The advantage of cold rolling is its cost-effectiveness.
Cold forming is 1 method, as well as machining and assembling. Cold forming is a unique process that allows the spline to be shaped to the desired shape. The resulting shape provides maximum contact area and torsional strength. Standard splines are available in standard sizes, but custom lengths can also be ordered. CZPT offers various auxiliary equipment, such as mating sleeves and flanged bushings.
Cold forging is another method. This method produces long splined shafts that are used in automobile propellers. After the spline portion is cut out, it is worked on in a hobbing machine. Work hardening enhances the root strength of the splined portion. It can be used for bearings, gears, and other mechanical components. Listed below are the manufacturing methods for splined shafts.
Parallel splines are the simplest of the splined shaft manufacturing methods. Parallel splines are usually welded to shafts, while involute splines are made of metal or non-metals. Splines are available in a wide variety of lengths and materials. The process is usually accompanied by a process called milling. The workpiece rotates to produce the serrated surface.
Splines are internal or external grooves in a splined shaft. They work in combination with keyways to transfer torque. Male and female splines are used in gears. Female and male splines correspond to 1 another to ensure proper angular correspondence. Involute splines have more surface area and thus are stronger than external splines. Moreover, they help the shaft fit into a grooved cylindrical member without misalignment.
A variety of other methods of manufacturing a splined shaft can be used to produce a splined shaft. Spline shafts can be produced using broaching and shaping, 2 precision machining methods. Broaching uses a metal tool with successively larger teeth to remove metal and create ridges and holes in the surface of a material. However, this process is expensive and requires special expertise.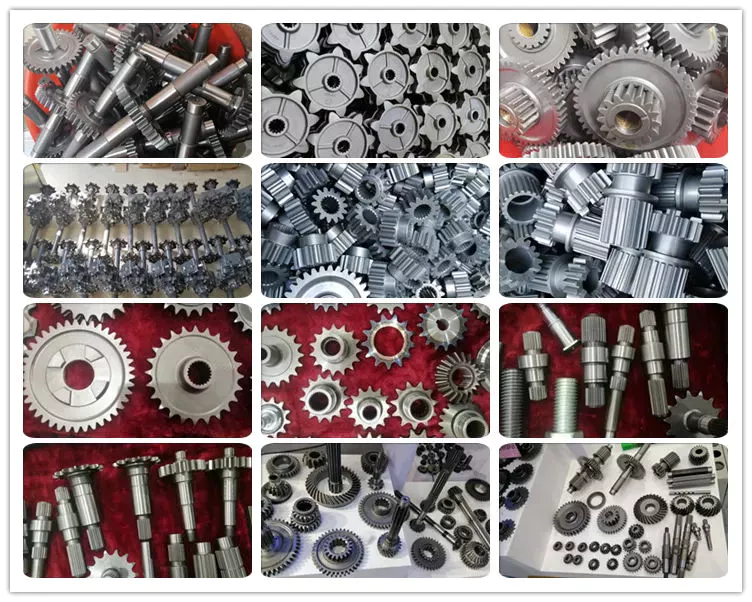
Applications
The splined shaft is a mechanical component with a helix-like shape formed by the equal spacing of grooves in a circular ring. The splines can either have parallel or involute sides. The splines minimize stress concentration in stationary joints and can be used in both rotary and linear motion. In some cases, splines are rolled rather than cut. The latter is more durable than cut splines and is often used in applications requiring high strength, accuracy, and smooth finish.
Splined shafts are commonly made of carbon steel. This alloy steel has a low carbon content, making it easy to work with. Carbon steel is a great choice for splines because it is malleable. Generally, high-quality carbon steel provides a consistent motion. Steel alloys are also available that contain nickel, chromium, copper, and other metals. If you’re unsure of the right material for your application, you can consult a spline chart.
Splines are a versatile mechanical component. They are easy to cut and fit. Splines can be internal or external, with teeth positioned at equal intervals on both sides of the shaft. This allows the shaft to engage with the hub around the entire circumference of the hub. It also increases load capacity by creating a constant multiple-tooth point of contact with the hub. For this reason, they’re used extensively in rotary and linear motion.
Splined shafts are used in a wide variety of industries. CZPT Inc. offers custom and standard splined shafts for a variety of applications. When choosing a splined shaft for a specific application, consider the surrounding mated components, torque requirements, and size requirements. These 3 factors will make it the ideal choice for your rotary equipment. And you’ll be pleased with the end result!
There are many types of splines and their applications are endless. They transfer torque and angular misalignment between parts, and they also enable the axial rotation of assembled components. Therefore, splines are an essential component of machinery and are used in a wide range of applications. This type of shaft can be found in various types of machines, from household appliances to industrial machinery. So, the next time you’re looking for a splined shaft, make sure you look for a splined one.


China best Powerful Factory Customization And Careful Creation Drive Transmission Drive Shafts with Free Design Custom
Product: ECOSPORT, Accent, Swift, COROLLA
12 months: 2017-2019, 2018-2019, 0AM927769D 0am mechatronic tcm de 0am gearbox full gearbox dsg 7 dq200 0am regener tcm nuev kit reparacion for volkswagen 2011-2016, 2012-2571, 2016-2571
OE NO.: 4213-5710
Car Fitment: Ford, Toyota, SUZUKI, Common BF Variety Aluminium Timing Pulley Hyundai
Dimension: .8M
Content: Metal
Design Variety: 2571061601
Guarantee: 1 Months
Merchandise Identify: Generate Shaft
Type: propeller shafts
OEM: Accpet
Top quality: Prime
Key word: push shafts
Shade: Black
Implement for: Universal Driver Shaft
Benefit: cardan shaft
Situation: Model new
Item: shaft travel
Packaging Details: 23.8 x 8 x 8 cm16.3 kg
Port: Primary ZheJiang /HangZhou
ODM&OEMAcceptedMerchandise identifyPush ShaftDealNormal or personalizedGainSeasoned factory A lot more Merchandise Firm Profile Support Customization&OEM Manufacturing Products Certifications Packaging And Logistics FAQ Q1: Are you trading firm or manufacturing unit? A1:We are OEM manufacturing facility. Q2: Can you produce or modify the propeller shaft we want? A2:Sure, Samples for improvement are warmly welcomed. We have abundant expertise in building and modifying the shafts.Q3:What is Moq for each objects.If we have in inventory?A3:Sample take a look at and sample orders could be recognized.Usually MOQ is 1pcs.Q4: How can l be positive the areas fit my car?A4:Make sure you tips the parts no to our product sales,and validate with them.Merely ship theimages of the areas to our income or inquire our revenue to deliver you image to verify.Q5:What other provider can you offer you?A5:OEM provider, PS70 1 stages Planetary gearbox ratio 3,4,5,6,8,ten we often warmly welcome customer to ship us samples to create a new item line.
What is a driveshaft and how significantly does it expense to substitute 1?
Your vehicle is manufactured up of a lot of shifting elements. Understanding every portion is crucial because a broken driveshaft can critically damage other areas of the vehicle. You may possibly not know how crucial your driveshaft is, but it’s important to know if you want to correct your auto. In this article, we are going to discuss what a driveshaft is, what its symptoms are, and how a lot it charges to change a driveshaft.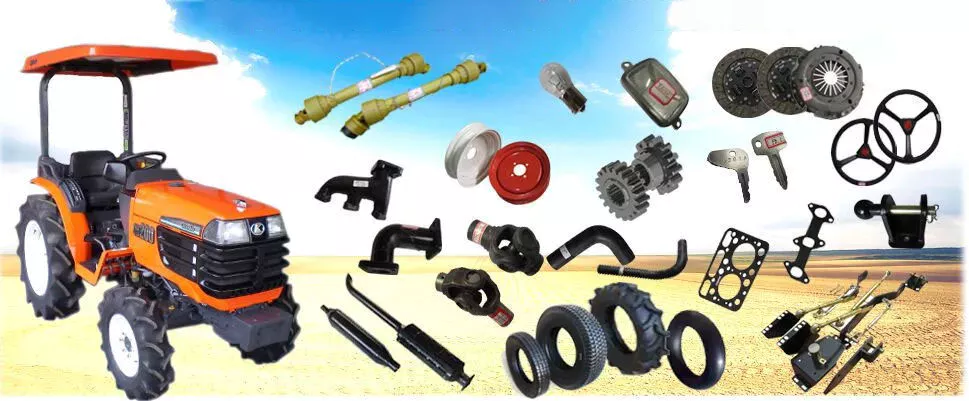
Restore broken driveshafts
A ruined driveshaft does not let you to change the wheels freely. It also exposes your automobile to higher restore expenses because of to ruined driveshafts. If the drive shaft breaks whilst the auto is in motion, it may possibly result in a crash. Also, it can considerably affect the functionality of the car. If you never resolve the problem appropriate away, you could chance a lot more high-priced repairs. If you suspect that the travel shaft is damaged, do the subsequent.
Very first, make certain the travel shaft is protected from dust, dampness, and dust. A proper driveshaft cover will avoid grease from accumulating in the driveshaft, decreasing the opportunity of more hurt. The grease will also cushion the metal-to-metallic get in touch with in the consistent velocity joints. For instance, hitting a comfortable substance is far better than hitting a metal wall. A damaged prop shaft can not only trigger hard cornering, but it can also lead to the car to vibrate, which can more injury the rest of the drivetrain.
If the driveshaft is ruined, you can choose to repair it by yourself or just take it to a mechanic. Generally, driveshaft repairs cost all around $200 to $300. Elements and labor could differ dependent on your car kind and sort of fix. These areas can value up to $600. Even so, if you never have a mechanical history, it is much better to leave it to a expert.
If you notice that one of the two travel shafts is worn, it is time to repair it. Worn bushings and bearings can cause the generate shaft to vibrate unnecessarily, causing it to break and result in further injury. You can also examine the center bearing if there is any play in the bearing. If these indicators take place, it is ideal to consider your car to a mechanic as shortly as possible.
Understand about U-joints
Even though most vehicles have at least one type of U-joint, there are other kinds obtainable. CV joints (also acknowledged as hot rod joints) are used in a selection of applications. The minor axis is shorter than the key axis on which the U-joint is found. In the two instances, the U-joints are lubricated at the manufacturing facility. During servicing, the generate shaft slip joint should be lubricated.
There are two major styles of U-joints, such as solid and push in shape. They are normally held in spot by C-clamps. Some of these U-joints have knurls or grooves. When deciding on the appropriate fitting, be certain to measure the entire fitting. To make sure you get the correct measurement, you can use the dimensions chart or check out the manual for your distinct product.
In addition to lubrication, the situation of the U-joint need to be checked routinely. Lubricate them frequently to stay away from premature failure. If you hear a clicking seem when shifting gears, the u-joint room may possibly be misaligned. In this scenario, the bearing could require to be serviced. If there is insufficient grease in the bearings, the common joint could need to have to be replaced.
U-joint is an essential part of the auto transmission shaft. Without them, your automobile would have no wheeled suspension. Without them, your motor vehicle will have a rickety entrance stop and a wobbly rear conclude. Simply because cars can’t drive on extremely-flat surfaces, they require flexible driveshafts. The U-joint compensates for this by making it possible for it to move up and down with the suspension.
A proper inspection will decide if your u-joints are loose or worn. It should be effortless to pull them out. Make positive not to pull them all the way out. Also, the bearing caps need to not go. Any indications of roughness or put on would reveal a require for a new UJ. Also, it is important to notice that worn UJs can not be fixed.
Symptoms of Driveshaft Failure
One particular of the most typical difficulties connected with a faulty driveshaft is difficulty turning the wheels. This seriously boundaries your all round manage more than the motor vehicle. Fortunately, there are numerous signs that could point out that your driveshaft is failing. You need to just take immediate steps to decide the trigger of the dilemma. 1 of the most typical leads to of driveshaft failure is a weak or faulty reverse gear. Other widespread brings about of driveshaft harm include driving way too difficult, obtaining trapped in reverse equipment and differential lock.
An additional signal of a unsuccessful driveshaft is strange sound while driving. These noises are generally the outcome of use on the bushings and bearings that support the drive shaft. They can also lead to your car to screech or scratch when switching from drive to idle. Dependent on the speed, the noise might be accompanied by vibration. When this happens, it really is time to ship your vehicle in for a driveshaft substitution.
One of the most typical signs of driveshaft failure is noticeable jitter when accelerating. This could be a sign of a unfastened U-joint or worn heart bearing. You must thoroughly inspect your automobile to figure out the trigger of these seems and corresponding signs. A licensed mechanic can assist you decide the cause of the sounds. A broken propshaft can severely limit the drivability of the car.
Normal inspection of the drive shaft can prevent severe hurt. Depending on the injury, you can substitute the driveshaft for anyplace from $500 to $1,000. Relying on the severity of the injury and the stage of fix, the cost will rely on the number of parts that need to have to be changed. Do not travel with a bad driveshaft as it can lead to a serious crash. There are several methods to avoid this problem totally.
The 1st symptom to appear for is a worn U-joint. If the U-joint arrives loose or moves too a lot when attempting to turn the steering wheel, the driveshaft is faulty. If you see obvious rust on the bearing cap seals, you can take your car to a mechanic for a thorough inspection. A worn u-joint can also point out a dilemma with the transmission.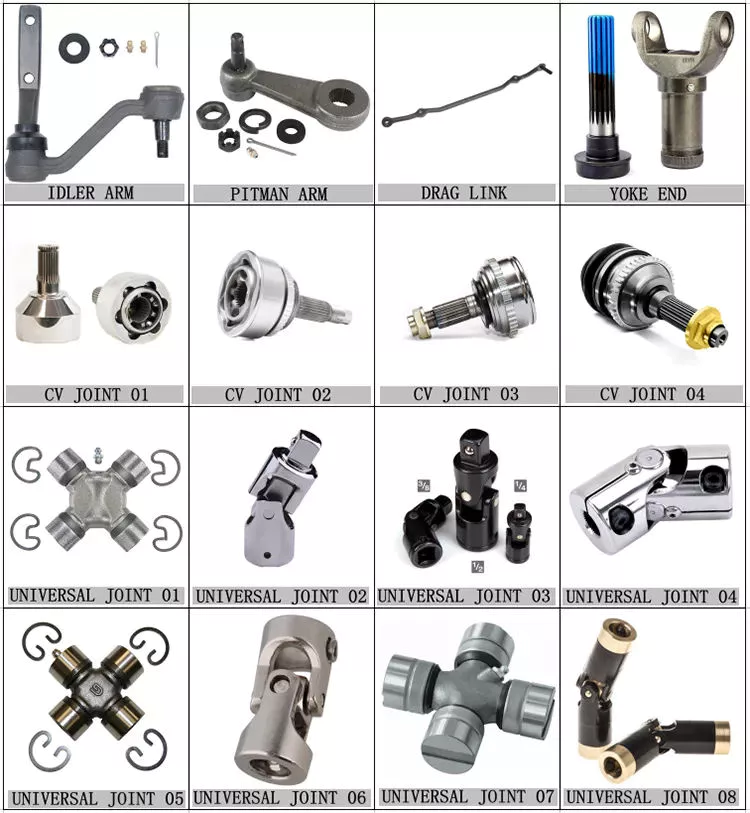
The cost of replacing the push shaft
Dependent on your condition and support heart, a driveshaft mend can value as tiny as $three hundred or as substantial as $2,000, dependent on the details of your auto. Labor charges are typically all around $70. Costs for the elements themselves selection from $four hundred to $600. Labor fees also differ by design and automobile make. In the long run, the decision to fix or substitute the driveshaft will rely on whether you want a fast automobile fix or a total auto mend.
Some automobiles have two separate driveshafts. One particular goes to the front and the other goes to the again. If your vehicle has four wheel travel, you will have two. If you are changing the axles of an all-wheel-push automobile, you’ll require a specific part for each and every axle. Choosing the incorrect a single can consequence in more high-priced repairs. Ahead of you start searching, you should know just how much it will value.
Depending on the kind of car you own, a driveshaft alternative will cost in between PS250 and PS500. Luxury vehicles can cost as a lot as PS400. Even so, for basic safety and the overall functionality of the auto, replacing the driveshaft may possibly be a essential restore. The value of changing a driveshaft depends on how prolonged your vehicle has been on the street and how much dress in and tear it has skilled. There are some signs that reveal a faulty push shaft and you should get immediate action.
Repairs can be expensive, so it’s ideal to employ a mechanic with expertise in the discipline. You will be investing hundreds of bucks a thirty day period, but you will have peace of brain understanding the work will be completed proper. Remember that you may possibly want to inquire a pal or family members member to support you. Depending on the make and product of your vehicle, replacing the driveshaft is more high-priced than replacing the components and carrying out it your self.
If you suspect that your travel shaft is damaged, be confident to correct it as shortly as attainable. It is not a good idea to travel a auto with irregular vibration and seem for a long time. Luckily, there are some swift ways to correct the difficulty and stay away from high priced repairs later on. If you’ve got seen the indicators earlier mentioned, it is really worth acquiring the job carried out. There are a lot of indications that your driveshaft could need to have service, which includes lack of electrical power or difficulty shifting the car.

